
Dear Sir or Madam,
Today we would like to inform you about newly published FOSTA final reports from the fields of mobility, construction as well as plant and mechanical engineering.
These and all other FOSTA reports can be found at shop.stahldaten.de
We would like to wish you now an interesting reading.
Above all, after this challenging year for all of us, we wish you and your families a Merry Christmas and a Happy and especially Healthy New Year 2021!
Your FOSTA team
| P 1064 - Economic production of weight-optimized and load-adapted functional components by incremental sheet-bulk metal forming
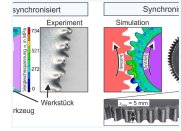
The objective of the research project is the economic production of industrially relevant functional components by incremental sheet-bulk metal forming by using the advantages of strain hardening. With regard to the current state of the incremental forming approach, the processing time has to be reduced significantly in order to achieve realistic cycle times.
With the acceleration of the process, changes of the thermal boundary conditions of the process are associated and need to be analyzed in the context of this research project. Applying new strategies, the effects on the adjustable component properties shall be determined experimentally and numerically so that the associated negative aspects of a subsequent heat treatment can be avoided and the costs can be reduced. read more
|
| P 1126 - Determination of the load-carrying capacity of innovative steel shells under realistic consideration of welding distortion
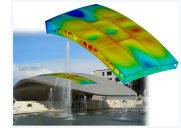
Stiffened shell structures (also Monocoque) are now being increasingly used in steel structures. Due to the use of slender metal sheets, the buckling influence needs to be taken into account. A geometrically and materially nonlinear analysis of the imperfect shell (GMNIA) corresponds to the theoretically highest degree of realism. The quality of proofs depends decisively on whether the imperfections introduced into the computational model adequately describe the effect of the imperfections of real structures.
Today, it is basically possible to reliably predict welding process influences by means of welding simulation. The extensive modelling and high computational effort, however, prevent its practical application. The analytical-numerical hybrid model provides a practical methodology for the welding simulation of large structural components. From the point of view of the design an interface to the welding simulation is to be realized and approved. read more
|
| P 1183 - Inductive welding of metallurgically plated sheets
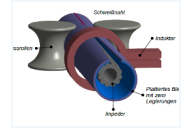
The research project opts to enable inductive longitudinal welding of metallurgically plated sheets for the production of cladded steel pipes. Thus, induction welding of multilayered steel compounds will be qualified for the first time. To obtain a consistent joint and a desired distribution of alloying elements along the joining zone, the different layer-materials have to be heated selectively and the weld pool movement in the heat affected zone has to be controlled. For this purpose, simultaneous multi-frequency technology is used for selective heating. Specific weld seam geometry controls the flow of the melt. A multiple simulation approach is used to reproduces the real process.
The multiple simulation approach combines numerical FEM simulation as well as conductive and inductive welding tests. The first module for inductive welding of multimaterials and multi-frequency technology will be the result of the simulation work. read more
|
| P 1237 - Extension of the process limits for wrinkle-free seaming of cans made of high-strength packaging steel

With the background of constantly decreasing resources and very high production volumes in the billions, the topic of material savings is of central importance in the packaging steel industry. The entire packaging steel industry is faced with the economic and technical challenge of having to process higher-strength tinplate alloys in a reliable manner. Within the scope of this research project, it was investigated to what extent thinner, higher-strength metal packaging materials can be processed reliably with the seaming technology in particular for three-piece food cans.
Based on extensive literature research on the state of the art of seaming technology for metal packaging and the expert discussion (interviews) within the industrial working group accompanying the project, the main influences on the seaming process have been detailed and evaluated. With help of an FEM process model for the roll-seaming technology, the main influences were analyzed and subsequently an optimization for the essential parameters was carried out. read more
|
| P 1267 - Proof of the applicability of resistance spot welding for reduced flange widths in lightweight optimized steel body-in-white construction
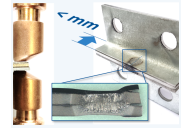
Lightweight construction concepts made of modern high-strength steel materials play an important role in the realization of resource-saving, affordable mobility. In order to increase customer benefits (door entry, "slim A-pillar", etc.) and reduce weight, there is also a growing interest in body construction in reducing the flange widths that are common today. The reliable and cost-efficient joining of components made of high-strength steels with reduced flange widths using the highly efficient resistance spot welding process widely used in the sheet steel processing industry represents a challenge.
By means of experimental and numerical investigations on joining tasks close to reality for car body construction beyond the current state of the art, the applicability of resistance spot welding for reduced flange widths was systematically investigated in this project. At the same time, the boundary conditions to be observed and economic compromises for a process capability suitable for production were determined. read more
|
|
|
|







