|
Dear Sir or Madam,
Today we would like to inform you about newly published FOSTA final reports from the fields of mobility, construction as well as plant and mechanical engineering.
These and all other FOSTA reports can be found at shop.stahldaten.de
We would like to wish you now an interesting reading.
Your FOSTA team
| | P 1033 – Fatigue design of rails based in fracture mechanics (IGF-No 18094 N)

In this research project, approaches for the fracture-mechanical description of crack growth in the rail foot are being developed. For this purpose, finite element simulations are used to show how the stresses from residual stresses, temperature, train passage and structural deformation are distributed in the rail foot. The magnitude of the loads to be applied from structural deformation is determined. It can be shown that the stress components can be divided into three groups according to their distribution in the rail foot, which can then also be found in the determination of the K-factors. Finally, the connection between torsion and displacement of the bridge head is examined in more detail. The residual stresses of the rails are determined experimentally. It is shown that the expected compressive residual stresses at the rail foot edge are also found in reality. more information
|
| P 1038 – Series-production of inductively heated blanks for hot sheet metal forming (IGF-No 18738 N)
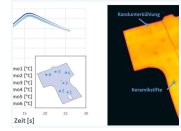
The aim of the project was to develop an inductive process for the flexible heating of near-series real components for the press hardening process. In the first work step, the typical component geometries of the blanks of press-hardened components were therefore provided by the committee accompanying the project. These were classified and categorised by the research centres. The resulting component catalogue served on the one hand as the basis for selecting the demonstrator component to be manufactured and on the other hand provided the boundary conditions for the simulation and design of the induction process. A B-pillar was chosen as a representative component to produce the demonstrator component. Due to the low power of the inverter provided in the project, it was decided to limit the investigations to the head of the B-pillar. more information
|
| P 1098 – Building Redevelopment – Solutions for Roof and Façade Systems using Lightweight Steel Constructions (IGF-No 18623 N)

Energy related refurbishments and building in existing structures gain in the framework of climate protection policy in importance. Various studies show that a significant reduction of emissions and energy consumption in the building sector can only be achieved by the refurbishment of existing buildings. Particularly upon industrial and commercial buildings, the thermal and energetic quality of the building envelope realized in the past often no longer meet the current and future requirements. In this research project the approach to carry out the energetic refurbishment during operation (without cost-intensive downtime) is pursued. In order to improve the thermal quality of the existing façade, additional heat-insulating components should be installed on the outside. Particularly promising is the use of building systems in lightweight steel or metal construction. more information
|
| P 1136 – Use of friction stir welding for joining of steels of different grade, in connection to a simultaneous development of appropriate new ceramic tools (IGF-No 19213 N)

The most important and first development goal in the project was the economic expansion of friction stir welding (FSW) for joining steel materials, also with high strengths. A lot of experience, which is available at the SLV Berlin-Brandenburg and also experimental applications were included in the project. Due to inquiries, mainly from the fields of shipbuilding, offshore, vehicle construction and special applications and demands of the project accompanying committee (PA), steel joints of different grades were welded and examined. To name a few of them: S235, S355, S690, CrNi18-10 and H800. Blind seams, butt joints and lap joints were welded. more information
|
| P 1236 – Quantification of the toughness influence on crack arrest properties of modern linepipe steels (IGF-No 19581 N)
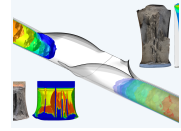
The resistance to brittle fracture initiation and long-running ductile fracture propagation are the most important safety requirements for gas transporting pipelines. To meet these requirements, pipeline steels with excellent toughness properties have been developed.
However, due to the brittle fracture phenomena occurring in the Charpy impact tests and the Battelle drop weight tear tests during the experimental toughness quantification the conventional design procedures for a comprehensive use of these excellent properties have to be reviewed. The phenomena include so called separations and inverse fracture behaviour, both of which have been assigned to the brittle failure mechanism. In addition, the ductile crack arrest needs to be ensured by a sufficient material resistance to fracture propagation, which is defined by the Charpy upper-shelf toughness. more information
|
| P 806 – Characterization and simplified modeling of the fracture behavior of spot welds from ultra-high strength steels for crash simulation with consideration of the effects of the joints on component behavior (S 24/10162/08 / A 262)
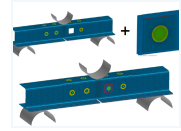
High and ultra-high strength steels are increasingly used in the automotive industry in thin sheet thicknesses for lightweight constructions, an increase in passive safety and conservation of energy. Hot stamped components made of 22MnB5 with a tensile strength up to 1500 MPa are already established in automobile engineering and the steel development is going towards even higher strength press hardened steels. The lightweight steel construction has a high potential to increase the energy efficiency even more. At present and also in future the well-established and highly automatable resistance spot welding process is used to join the single components of high strength steels to the load bearing construction. more information
|
| P 1284 – Assessment on the utilization of corrugated cardboard as an ecological core material for sandwich panels (IGF-No 19886 N)
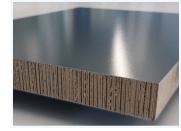
Within the scope of the research project the utilization of corrugated cardboard as an alternative core material for sandwich panels was assessed. On the basis of a literature research the most important basics of paper and corrugated cardboard on the one hand and of sandwich constructions on the other hand were collected. Building on this a viable material model was found and the elastic parameters as well as the strengths for overall ten different types of cardboard were detected. The experiments for the determination of the elastic material model could not be evaluated tatistically due to the small number of tests. Despite partly high deviation of the test results, a fundamental assessment of the bearing behaviour was possible, though. more information
|
| P 1238 – Local material influence on presshardened steel to improve joinability of 22MnB5 parts (IGF-No 19797 BG)
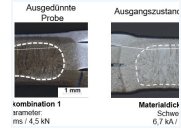
The aim of the research project was to extend the joinability of hot-stamped components made of 22MnB5 by the targeted application of a local thinning. In addition to the local reduction of the material thickness, the material properties were influenced in this area by the formation of deformation-induced-ferrite (DIF). For this purpose, the IFUM Hannover carried out investigations on the hot-stamping of locally deformed blanks. The focus of the IMF Magdeburg was on the extension of the joinability of material combinations with 22MnB5 by resistance spot welding as well as self-pierce riveting.
At the beginning of the project, extensive tests were carried out on a forming dilatometer to determine the process window of DIF formation. The results of the dilatometer investigations were then validated by experimental thinning tests. For this purpose, experiments were carried out on a hydraulic double-column press of the Dunkes company, in which embossing was applied to the blanks by means of a deformation plate in a conventional hot-stamping process. more information
|
|
|
|










