|
Dear Sir or Madam,
Today we would like to inform you about newly published FOSTA final reports from the focal areas of mobility, construction as well as plant and mechanical engineering. You can find these and all other FOSTA reports in the Matplus Shop.
We wish you an interesting reading.
Your FOSTA team
| P 1281 – Integral and holistic planning of road bridges based on hierarchial models (S 024/10245/17)

The IntegBridge research project develops a semi-automated, computer-based method for the holistic assessment of bridge design alternatives across their entire life cycle. By linking data sources (Linked Data) and using BIM models, the ecological, economic, and socio-economic impacts of bridge variants are calculated. BIM components are connected to pre-assessed elements that represent different levels of detail and provide data on costs, environmental impacts, and construction times. Maintenance strategies are automatically integrated into the models as follow-up elements. The models can be transferred to the IntegBridge software via ODBC or IFC interfaces, where additional input (e.g., traffic data, discount rate) is added. Socio-economic costs, mainly caused by traffic disruptions and time losses, are calculated using a deterministic queuing model. The developed workflow enables early and comprehensive comparison of bridge variants, allowing for continuous optimization during planning—with the goal of implementing not the cheapest, but the most site-appropriate and sustainable solution. more information
|
| 1488 – Validation of methods to avoid liquid metal embrittlement on realistic principle components (IGF-No 21483 BG)
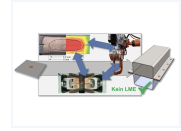
This project investigated the susceptibility to Liquid Metal Embrittlement (LME) of dual-phase steel under various conditions, using RSW-based tests and Gleeble experiments. Increased welding time significantly intensified LME cracking, while pre-strain had no major effect. External loads during welding increased LME, as confirmed in both test setups. Offset welding proved to be the most critical disturbance and led to a new LME crack type. Numerical studies enabled the development of an optimized welding program to avoid LME. Gleeble tests showed that higher temperatures intensified LME, while increased strain and heating rates, as well as elastic pre-stress, reduced it. Plastic pre-stress increased LME, while no LME occurred at 850 °C and 3 s holding time. Three-point bending tests on prototype components revealed reduced load capacity and energy absorption in LME-affected samples, confirmed by simulations. more information
|
| P 1513 – Method development for the design of bonded joints made of high-strength steel, taking into account operationally relevant stresses in mechanical and plant engineering (IGF-No 21445 N)

Adhesive bonding is still rarely used in agricultural machinery and plant engineering, especially for joining thicker sheet metal (3–10 mm), despite being established in other fields. A key obstacle is the lack of experience in designing bonded joints and limited knowledge about factors like resistance to agricultural media. This research project examined how structural bonding can efficiently utilize the strength of joints made from high-strength steels in 5 mm thick constructions under vibration loads. The goal was to develop a design method suitable for SMEs, based on the FKM guideline. Various factors affecting the quasi-static and dynamic strength of bonded joints were analyzed. These findings formed the basis for an analytical design method, which was successfully verified and used to derive SME-relevant design and strength guidelines. more information
|
| P 1521 – Integral sheet piling abutments of modular composite bridges for a time efficient construction (S 024/10624/20)
The report summarizes investigations into the development of a design concept for integral frame corners in composite bridges with sheet pile abutments. The integral design enables an economical and low-maintenance construction by dispensing with bearings and joints. Sheet pile abutments also reduce construction costs. The FOSTA project P1521 developed a concept for this. It is based on an analysis of the German bridge stock, in which 80% of federal highway bridges have spans of less than 50 m - an area covered by the concept. Test series on separate frame corner sections showed high load-bearing capacities (up to 1200 kNm). Supplementary numerical analyses provided insights into load paths and influencing parameters. A final large-scale test confirmed the results and showed increased stress in the lower area. Finally, a design concept is presented and applied to an example with a span of 45 m. more information
|
| P 1529 – Process comparison for forming metallic bipolar plates – hollow embossing vs. hollow embossing rolling (IGF-No 21715 BR)
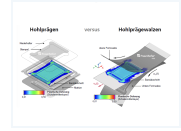
The research project provided fundamental insights into the mechanisms and limitations of roll embossing metallic bipolar plates (BPP) made from stainless steel foil. This still underexplored process offers the potential for higher production rates than conventional methods such as embossing and hydroforming. The study investigated the geometric limitations of roll embossing, estimated achievable cycle times, and compared them with results from conventional embossing. Initial analysis was conducted using FE simulations based on a defined demonstrator geometry, equipment, and tooling. These findings were implemented in tool design and process control, then validated through experimental trials. The evaluation of process and measurement data identified which geometric features can be accurately formed and which cycle times can be achieved within specified tolerances. Key results focus on formability, dimensional accuracy, and production speed. The project opens access to the growing BPP market, especially for SMEs, by enabling them to tailor products and services to the specific requirements of embossing and roll embossing. more information
|
| P 1530 – Extending the process boundaries in GMAW hot-wire welding by adapting the material and energy input using an upstream hot-wire preheating system (IGF-No 21716 BG)
Despite the widespread use of gas metal arc welding (GMAW) processes, they inherently couple material and energy input. This research project aimed to develop a GMAW hot wire process with upstream ohmic preheating of the filler wire to decouple these inputs. The goal was to enable precise control over material and energy input while increasing deposition rates. The optimized process was examined for its stability, weld quality, and suitability for joining, cladding, and additive manufacturing applications. A wire angle of 50° proved beneficial for uniform weld seams, while the GMAW arc itself was mainly influenced by electrical heating rather than the preheated wire. For additive applications, a wire angle of 65° and a preheating length under 30 mm were ideal. The process shows excellent suitability for single-layer welding of 8 mm thick mild steel sheets and also has great potential for welding thicker sheets (up to 20 mm). more information
|
| P 1537 – Wood-steel hybrid constructions using the example of bending-stressed structural elements (IGF-No 21722 N)
The construction industry is Germany’s largest CO₂ emitter. Wood, as a renewable material, can help replace CO₂-intensive materials. However, timber has limitations, especially for large spans. The research project “HoStaBau” addresses this by combining timber and steel to create hybrid elements with reduced cross-sections. Analytical and numerical studies confirmed the compatibility of both materials. 106 specimens were tested, showing that full bonding through adhesive methods is feasible and durable under stress, moisture, heat, and aging. In 4-point bending tests, hybrid beams showed up to 120% higher load capacity and 250% greater stiffness. Shear strength increased by up to 440% in 3-point tests. A design concept was developed, confirming full bonding and enabling a practical design method. This allows fast implementation, especially benefitting SMEs by providing them with an innovation edge. more information
|
| P 1561 – Modelling and Evaluation of Supply Chains for Hydrogen Transport for the Steel Industry with special consideration of transport-related Energy Losses (IGF-No 38 BG)
Large industrial consumers such as steel producers and the chemical industry can significantly reduce their CO₂ emissions by substituting fossil energy sources with hydrogen. Switching to direct reduction in steel production requires large volumes of green hydrogen, but large-scale hydrogen supply remains largely unexplored. Additional uncertainties arise from various ramp-up scenarios on both the production and consumption sides. This research project analyzes hydrogen logistics chains, taking into account loss factors that are particularly relevant due to hydrogen’s volatile nature. Fraunhofer CML investigates transport chains, while Fraunhofer IGP develops simulation models for different loss mechanisms. A planning tool for pipeline dimensioning was created, supported by models for alternative transport modes such as trucks or trains. Simulations show that energy and cargo losses—especially with liquid hydrogen (LH₂)—significantly influence the economic choice of transport. The first validated holistic logistics simulation models have been developed and are ready for further use cases. more information
|
|
|
|





